Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is one of the most common oral health conditions affecting adults worldwide. While many people assume bleeding gums or bad breath are minor dental issues, untreated gum disease can lead to severe oral damage and has been linked to serious overall health problems.
In this article, we’ll explain what gum disease is, the warning signs to watch for, and how it can impact your total health — not just your smile.
What Is Gum Disease?
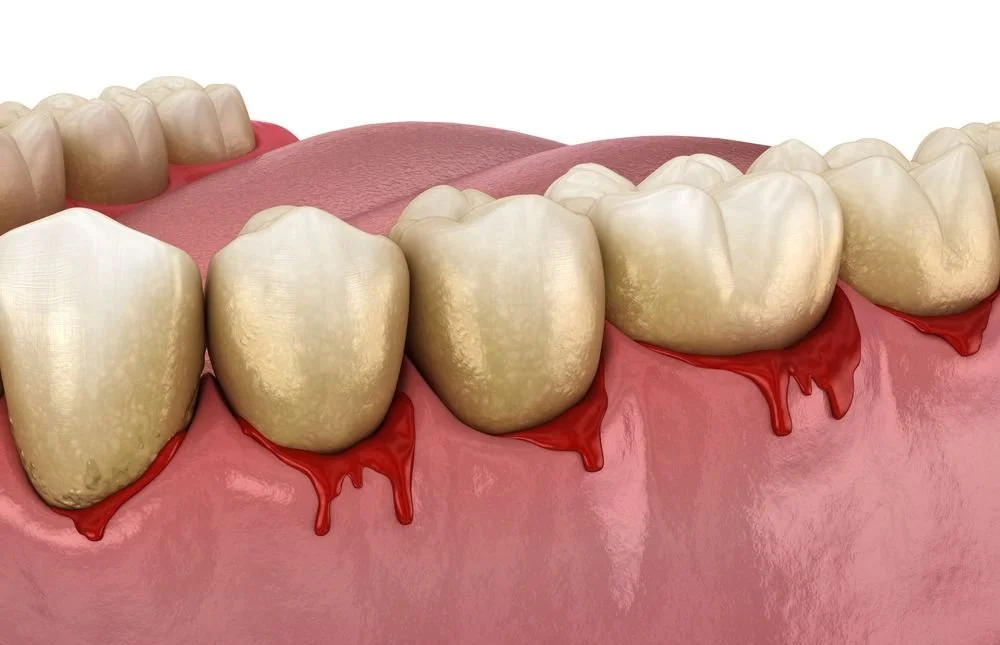
Gum disease is an infection of the tissues that support your teeth. It’s caused by plaque buildup — a sticky film of bacteria that forms on teeth when oral hygiene is inadequate.
There are two main stages:
1. Gingivitis (Early Gum Disease)
Red, swollen, or tender gums
Bleeding when brushing or flossing
Persistent bad breath
Gingivitis is reversible with proper dental care and professional cleanings.
2. Periodontitis (Advanced Gum Disease)
Gum recession (gums pulling away from teeth)
Loose or shifting teeth
Pus between gums and teeth
Pain when chewing
At this stage, the damage is permanent and may lead to tooth loss if untreated.
Warning Signs of Gum Disease You Shouldn’t Ignore
Many people don’t feel pain in the early stages of gum disease, which is why it often goes unnoticed. Watch for these key symptoms:
Bleeding gums (especially during brushing or flossing)
Chronic bad breath or bad taste in the mouth
Swollen, red, or tender gums
Gums that appear to be pulling away from the teeth
Loose teeth or changes in bite alignment
If you notice any of these signs, it’s important to see a dentist as soon as possible.
Health Risks Linked to Gum Disease
Gum disease doesn’t just affect your mouth. Research shows a strong connection between periodontal disease and several serious health conditions.
Heart Disease and Stroke
Bacteria from infected gums can enter the bloodstream and contribute to inflammation in blood vessels. This inflammation may increase the risk of:
Heart disease
Blocked arteries
Stroke
Diabetes Complications
People with diabetes are more prone to gum disease — and gum disease can make diabetes harder to control. The inflammation can interfere with blood sugar regulation, creating a dangerous cycle.
Respiratory Problems
Oral bacteria can be inhaled into the lungs, increasing the risk of:
Pneumonia
Chronic respiratory infections
Pregnancy Risks
Untreated gum disease has been linked to:
Premature birth
Low birth weight babies
Pregnant patients should pay extra attention to gum health during routine dental visits.
Weakened Immune System
Chronic infection in the gums forces the immune system to stay in a constant state of inflammation, potentially weakening the body’s ability to fight other infections.
How Gum Disease Is Treated
Treatment depends on the severity of the condition:
Professional dental cleanings to remove plaque and tartar
Scaling and root planing (deep cleaning below the gumline)
Antibacterial rinses or medications
Periodontal therapy or surgery for advanced cases
Early detection is key to preventing long-term damage.
How to Prevent Gum Disease
Good oral hygiene and regular dental care are your best defenses:
Brush twice daily with fluoride toothpaste
Floss every day
Use an antimicrobial mouthwash
Avoid tobacco products
Schedule regular dental checkups and cleanings
Final Thoughts: Don’t Ignore Gum Disease
Gum disease is more than a dental issue — it’s a serious health warning sign. Bleeding gums, chronic bad breath, or gum recession should never be ignored. With early treatment and consistent care, gum disease can be managed and its health risks reduced.
If you’re experiencing symptoms of gum disease, schedule a dental appointment today. Your smile — and your overall health — depend on it.
Take control of your gum health today.
Call 9558 8988, email info@painfreedentistsydney.com.au, or book online to schedule your dental consultation and prevent gum disease before it leads to serious health problems.